Functional NeuroCognitive Imaging
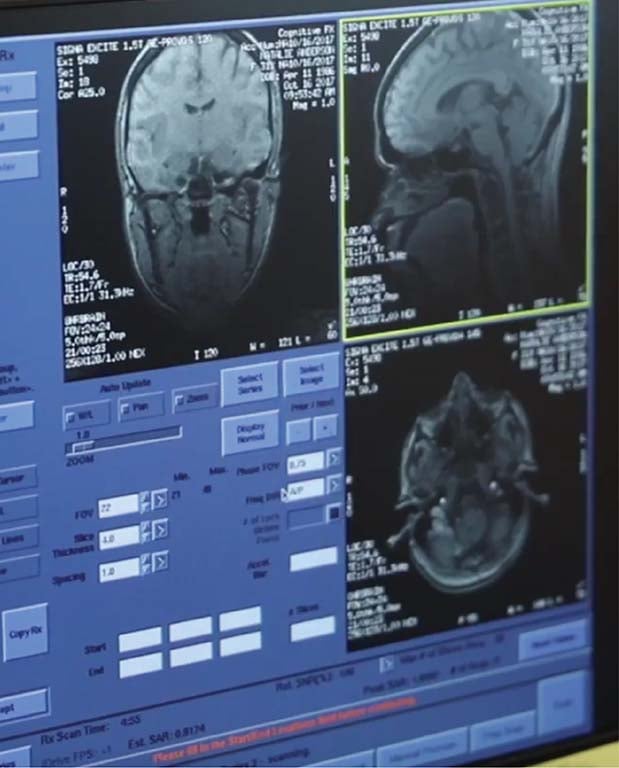


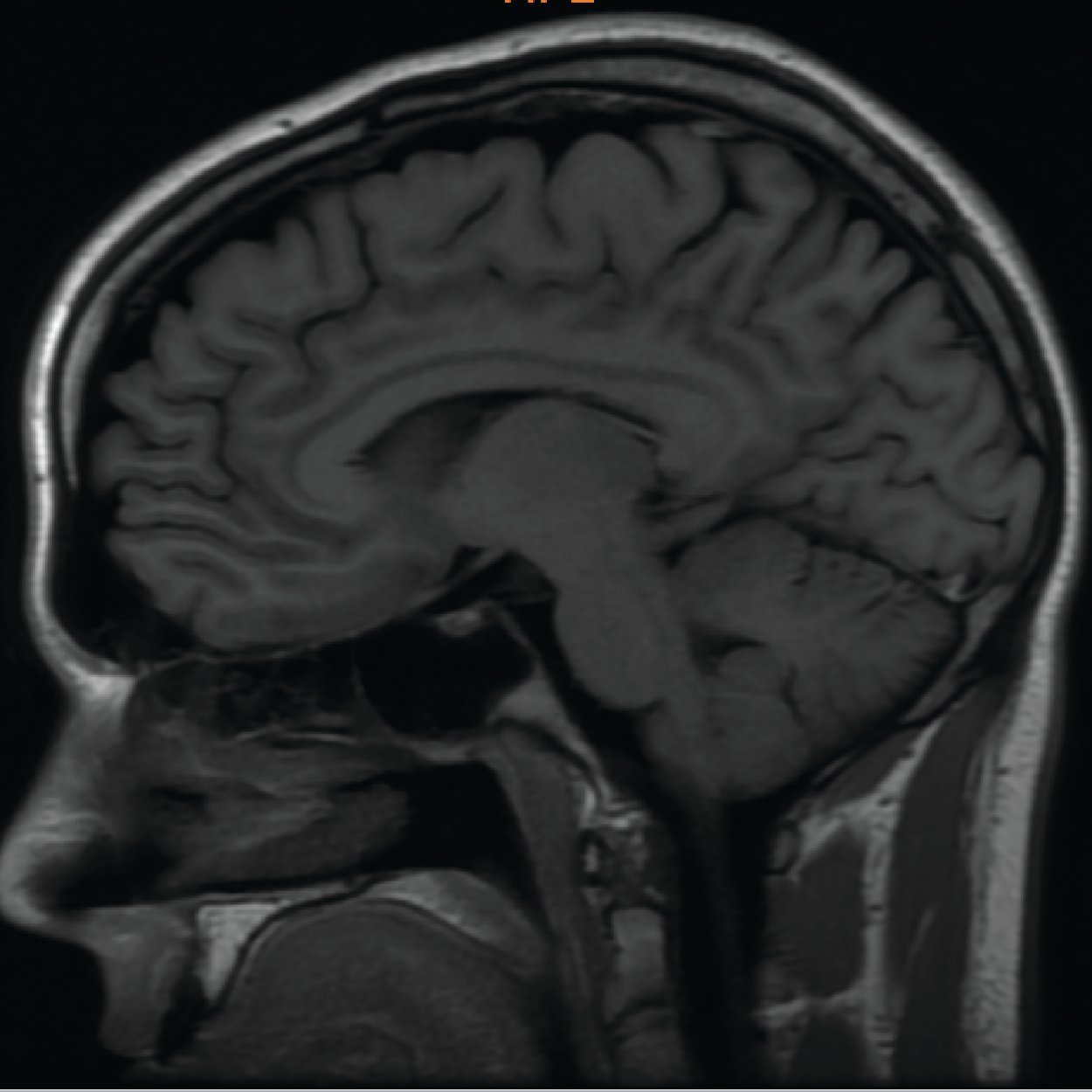
Functional NeuroCognitive Imaging or fNCI is a state of the art form of fMRI that empowers us to effectively treat concussions through targeted treatment.





What is fNCI?
fNCI is an advanced form of a functional MRI that has been standardized for clinical application. Cognitive FX's fNCI imaging and testing protocol includes three different cognitive tests performed inside an MRI machine. fNCI is measuring neurovascular coupling (NVC), which is the connection between neurons and blood in the brain.
fNCI is a method that takes continuous measurements of activation throughout brain over time during cognitive testing. By analyzing these brain activity measurements and comparing them to a healthy control database, we measure and understand the severity of an injury in each region of the brain.
What is NVC and why is it Important
Neurovascular Coupling (NVC) is the connection between neurons (brain cells) and blood vessels. Neurons need a lot of energy to do their job - blood vessels bring that energy to neurons. When an injury or neurological disorder occurs, the connection between blood vessels and neurons can be disrupted. This prevents some regions of the brain from receiving the necessary energy to perform. Also, when neurons aren’t working properly, they can fail to trigger increased blood flow to themselves. Together, we call this Neurovascular Coupling Dysfunction.
This results in post-concussion symptoms that include, but are not limited to, fatigue, headaches, attention difficulties, memory issues, sleep problems, and emotional distress.
Most clinics attempt to treat post-concussion syndrome by focusing on symptoms – which is a challenging diagnostic approach for effective treatments. To effectively treat PCS you must treat Neurovascular Coupling Dysfunction. This makes the fNCI brain scan such a powerful tool. fNCI scans show whether brain cells are triggering blood flow, and whether vessels are responding to this signal, while the brain is at work. fNCI detects these problems by determining whether activity levels in a patient match levels seen in healthy people in key regions of the brain.
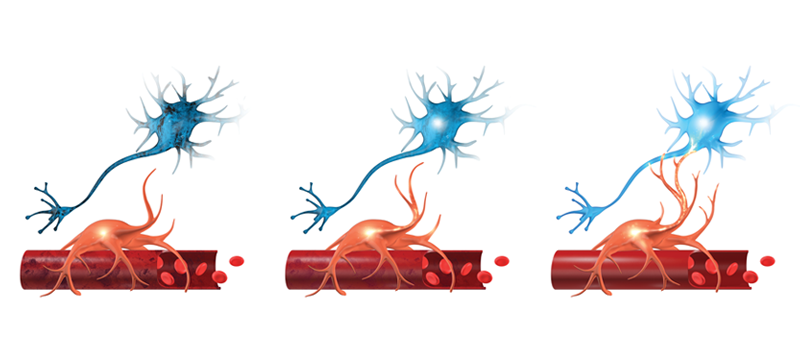
fNCI Measurements

Functional Systems
The brain is composed of hundreds of specialized regions. Each region is dedicated to carrying out a specific function. However, any cognitive or motor activity that you do during daily activities is carried out by several regions that are connected to one another in a coordinated effort. We call these networks Functional Systems. Through our extensive research on concussions and fMRI, we have been able to determine 27 functional systems that are commonly affected by concussions or brain injuries.
Each functional system measures a set of specific brain regions that should be activated during that task, and the integrity of the connections between those regions. The brain regions and the connections are measured to ensure that neurons are responding correctly and triggering blood flow correctly to carry out the demands that are placed on the normal healthy brain.
Brain Regions
fNCI highlights which areas of the brain function normally and which areas are hypo-activated. A normal, non-injured, brain responds predictably to the challenges of performing each of the three cognitive tests, with an ideal healthy pattern being determined from the database of healthy controls. A response that is significantly lower is an indication of dysregulation in neurovascular coupling and represents a deficiency of neuronal activation, blood flow, or both in that area.
fNCI provides valuable insights to understand each patient’s brain. When we can see where the brain is underperforming in some areas, or overperforming in other areas to make up for it, we can target specific treatments to significantly restore the balanced sort of functioning seen in healthy brains.
Inter-Region Communication
To accomplish any cognitive task, regions of the brain work in a coordinated manner, passing information back and forth. Depending on the task, a given region must pay attention to and respond to signals coming from some brain regions and ignore signals coming from other brain regions. Healthy Inter-Region Communication means there is a correct balance of connections within a functional system during a given task.
Functional Systems
The brain is composed of hundreds of specialized regions. Each region is dedicated to carrying out a specific function. However, any cognitive or motor activity that you do during daily activities is carried out by several regions that are connected to one another in a coordinated effort. We call these networks Functional Systems. Through our extensive research on concussions and fMRI, we have been able to determine 27 functional systems that are commonly affected by concussions or brain injuries.
Each functional system measures a set of specific brain regions that should be activated during that task, and the integrity of the connections between those regions. The brain regions and the connections are measured to ensure that neurons are responding correctly and triggering blood flow correctly to carry out the demands that are placed on the normal healthy brain.
Regions of the Brain
fNCI highlights which areas of the brain function normally and which areas are hypo-activated. A normal, non-injured, brain responds predictably to the challenges of performing each of the three cognitive tests, with an ideal healthy pattern being determined from the database of healthy controls. A response that is significantly lower is an indication of dysregulation in neurovascular coupling and represents a deficiency of neuronal activation, blood flow, or both in that area.
fNCI provides valuable insights to understand each patient’s brain. When we can see where the brain is underperforming in some areas, or overperforming in other areas to make up for it, we can target specific treatments to significantly restore the balanced sort of functioning seen in healthy brains.
Inter-Region Communication
To accomplish any cognitive task, regions of the brain work in a coordinated manner, passing information back and forth. Depending on the task, a given region must pay attention to and respond to signals coming from some brain regions and ignore signals coming from other brain regions. Healthy Inter-Region Communication means there is a correct balance of connections within a functional system during a given task.