Most POTS Programs Manage Symptoms.
We Treat It at the Source.
Our 4‑day program targets the neurological root causes of POTS, aiming to provide long‑term regulation gains and quality of life improvements, not just short‑term symptom management.
Why POTS Treatment Needs a Neurological Lens (vs. Cardio‑Only)
Today’s healthcare system largely treats postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome (POTS) as a cardiovascular problem. We treat it as an autonomic nervous system regulation problem in the brain and brainstem that creates downstream cardio symptoms.
🧠
The autonomic nervous system (ANS) controls heart rate, blood pressure, and blood‑gas responses to posture changes.
🧠
The vestibular organs and cranial nerves feed those centers; miscalibration can lead to oversized heart rate and blood pressure response when standing.
🧠
Breathing mechanics and CO₂/O₂ balance strongly affect cerebral blood flow and tissue oxygen delivery.
How Our Program Is Different: We're Treating the Problems With a Different Tool Kit

We're not asking your body to adapt to dysfunction—we're retraining the dysfunction itself
Traditional approaches try to build tolerance around a broken system. Compression socks, salt loading, and slow cardio reconditioning help you cope with dysregulation, but they don't fix the autonomic nervous system that's causing it.
Our approach targets the brainstem and autonomic centers that are causing the exaggerated heart rate and blood pressure responses. We're recalibrating the thermostat, not just adjusting to a room that's always too hot.

We use tools that most POTS programs don't even consider
Therapeutic CO₂ use - Most providers see CO₂ as waste. We use it to improve oxygen delivery and teach your blood vessels to respond appropriately.

Vestibular recalibration - Your inner ear sensors tell your brain about position changes. When these are miscalibrated, your nervous system overreacts to standing. We directly retrain these sensors.
Cranial nerve activation - Strategic use of taste, smell, and sensory inputs to influence the brainstem centers that control heart rate and breathing in real-time.
Our interval-recovery method teaches your nervous system to switch gears
Standard reconditioning keeps you in moderate zones for long periods. Our Neuro-Cardio Training uses brief rounds working through all heart rate zones, including higher and lower, along with precise recovery. This teaches your sympathetic (gas pedal) and parasympathetic (brake pedal) systems to work together again—the core problem in POTS.
You're not just building stamina; you're retraining the autonomic reflexes themselves.
We have a specific origin story: concussion patients with POTS
This protocol wasn't invented for POTS—it was discovered while treating patients with post-concussion syndrome (PCS). We noticed our PCS patients with POTS symptoms were recovering their autonomic function through neurological rehabilitation. We then refined and formalized what was working into a dedicated POTS program.
This means our approach emerged from actual patient outcomes, not theory.

Four days of intensive, supervised recalibration vs. months of trial-and-error at home
Most programs send you home with general exercises and hope. We provide 4 days of hands-on, real-time adjustment of your treatment based on how your nervous system responds. Then you leave with a personalized protocol that's already been tested and refined on your specific dysregulation pattern.
The bottom line:
If you've tried cardiovascular reconditioning, medication management, and lifestyle modifications without lasting improvement, it's likely because those approaches aren't addressing the neurological regulation problem. We're treating a different layer of the problem—and that's why patients who've "tried everything" often see results they haven't experienced before.
Standard POTS Treatment Approach vs. Cognitive FX
| Most Healthcare Providers |
|
||
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Cardiovascular deconditioning — aims to gradually rebuild exercise tolerance through low-to-moderate steady-state cardio. | Neurological retraining — targets the autonomic nervous system (ANS) to restore proper regulation of heart rate, blood pressure, and breathing. | |
| Underlying Theory | POTS is a heart and blood vessel issue. | POTS is a form of dysautonomia — an ANS and regulation issue that manifests as cardiovascular symptoms. | |
| Treatment Tools | Salt tablets, high water intake, compression garments, medications, and gradual recumbent-to-upright cardio. | Multi-modal neurological retraining: Neuro Cardio Training, vestibular recalibration, cranial nerve activation, breathing mechanics, and carbon dioxide therapy. | |
| Cardio Method | Long-duration, low-intensity cardio focused on conditioning. | Proprietary Neuro-Cardio Training method that recalibrates and teaches the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems to work together again and respond appropriately to exercise. | |
| Vestibular Work | Rarely included or generalized balance work. | Targeted vestibular recalibration (especially saccule/vertical orientation) to reduce orthostatic overreaction. | |
| Breathing Approach | Basic relaxation or endurance breathing. | Retrains nasal/diaphragmatic mechanics and CO₂/O₂ balance to directly influence ANS function and blood flow. | |
| Cranial Nerve Integration |
Not addressed. | Activates smell/taste/trigeminal inputs to influence brainstem centers that regulate HR and breathing. | |
| CO₂ & Oxygen Use | Viewed as waste vs. intake gas; not targeted. | Uses CO₂ therapeutically (CarboHaler inhalation pre-cardio, CO₂ suit recovery) to improve oxygen delivery and vasodilation. | |
| Role of Medication | Central—used to manage HR, BP, and volume (beta blockers, fludrocortisone, midodrine, etc.). | Secondary—may supplement care but not required; goal is self-regulation without lifelong medication dependence. | |
| Program Goal | Manage symptoms and maintain functionality. | Retrain autonomic control and improve long-term quality of life. | |
| Duration of Program | Ongoing home program; indefinite. | 4-day intensive (evaluation + 3 treatment days) plus structured home continuation plan. | |
| Outcome Focus | POTS symptom stabilization. | System regulation and sustainable improvement in exercise tolerance and daily function. |
Most Healthcare
Providers
Cardiovascular deconditioning — aims to gradually rebuild exercise tolerance through low-to-moderate steady-state cardio.
CFX
Neurological retraining — targets the autonomic nervous system (ANS) to restore proper regulation of heart rate, blood pressure, and breathing.
Most Healthcare
Providers
POTS is a heart and blood vessel issue.
CFX
POTS is a form of dysautonomia — an ANS and regulation issue that manifests as cardiovascular symptoms.
Most Healthcare
Providers
Salt tablets, high water intake, compression garments, medications, and gradual recumbent-to-upright cardio.
CFX
Multi-modal neurological retraining: Neuro Cardio Training, vestibular recalibration, cranial nerve activation, breathing mechanics, and carbon dioxide therapy.
Most Healthcare
Providers
Long-duration, low-intensity cardio focused on conditioning.
CFX
Proprietary Neuro-Cardio Training method that recalibrates and teaches the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems to work together again and respond appropriately to exercise.
Most Healthcare
Providers
Rarely included or generalized balance work.
CFX
Targeted vestibular recalibration (especially saccule/vertical orientation) to reduce orthostatic overreaction.
Most Healthcare
Providers
Basic relaxation or endurance breathing.
CFX
Retrains nasal/diaphragmatic mechanics and CO₂/O₂ balance to directly influence ANS function and blood flow.
Most Healthcare
Providers
Not addressed.
CFX
Activates smell/taste/trigeminal inputs to influence brainstem centers that regulate HR and breathing.
Most Healthcare
Providers
Viewed as waste vs. intake gas; not targeted.
CFX
Uses CO₂ therapeutically (CarboHaler inhalation pre-cardio, CO₂ suit recovery) to improve oxygen delivery and vasodilation.
Most Healthcare
Providers
Central—used to manage HR, BP, and volume (beta blockers, fludrocortisone, midodrine, etc.).
CFX
Secondary—may supplement care but not required; goal is self-regulation without lifelong medication dependence.
Most Healthcare
Providers
Manage symptoms and maintain functionality.
CFX
Retrain autonomic control and improve long-term quality of life.
Most Healthcare
Providers
Ongoing home program; indefinite.
CFX
4-day intensive (evaluation + 3 treatment days) plus structured home continuation plan.
Most Healthcare
Providers
POTS symptom stabilization.
CFX
System regulation and sustainable improvement in exercise tolerance and daily function.
How Our POTS Evaluation & Treatment Works

Comprehensive POTS Evaluation
-
Functional testing of orthostatic response, vestibular function, cranial‑nerve inputs, and breathing mechanics.
-
Education about POTS, how neuro training helps, and how we’ll customize your treatment plan.

Multi-Modal Treatment (~4–5 hours/day)
-
Neuro-Cardio training to teach the ANS to switch gears.
-
Vestibular recalibration exercises that improve vertical‑change sensing and reduce orthostatic overreactions.
-
Breathing mechanics work to influence ANS function and blood flow.
-
Cranial-nerve stacking to steer autonomic tone.
-
End‑of‑day CO₂-based recovery suit for relaxation and tissue perfusion.
-
Planned rest blocks to protect tolerance.
Home program: You leave with daily drills and a repeatable interval‑recovery framework.
Patient Reviews
Jennifer H.
"Cognitive FX gave our daughter her life back! ... Cognitive FX is incredible; I can not adequately put into words how much we believe in their recovery program. We love the staff, and diagnostic measures, the recovery program, and the post-care follow up. I honestly can not think of one negative thing to say. The therapists are so attentive, skilled, caring and fun. Dr. Fong and RN Kaydee Severs are so incredibly smart, thorough in their explanations and exceptionally compassionate."
Review Source:
https://g.co/kgs/B5hSJ8
Liesel G.
"Everyone was super nice and encouraging. The therapies were tailored to my individual strengths, weaknesses, and needs. I have had significant improvement and my last FMRI came back looking significantly better than the first one. I feel like I am getting back to my old self after nearly 5 years of problems and pain. I'm so grateful to everyone at Cognitive FX who helped me on my journey!"
Review Source:
https://g.co/kgs/5SLZpJ
Will H.
"This place saved the life of someone we love. I was so impressed with the level of professionalism and care that we received. This facility is a blessing and I wouldn't hesitate at all to work with this team."
Review Source:
https://g.co/kgs/Hz35Pp
Chidinma O.
"Cognitive Fx is a great place to receive treatment for post-concussive syndrome. They definitely listen to all the symptoms you experience in an objective manner. Their exams provide great validation of the weird post-concussive symptoms that neurologist typically have a hard time diagnosing. Also, just after a few days of treatment, I began noticing improvements on my symptoms. I’m very thankful for Cognitive Fx and I look forward to their science and research being utilized more in the treatment of brain injuries and complications."
Review Source:
https://g.co/kgs/W15sui
Michelle F.
"...EPIC treatment at Cognitive FX was a lifesaver. I was shocked at how much better I felt after my week there! The fog lifted and the fatigue finally began to let up. I could focus, read, and attend better. I felt like myself! When the fNCI scan scientifically backed up what I was feeling, I cried with joy! The entire team is great! Everyone was so caring and helpful! The value of brain function is well worth the cost. I would recommend anyone who is struggling with PCS to meet with Dr. Fong. It was worth every penny I paid and more! I continue to work the program for brain health given to me when I completed the treatment."
Review Source:
https://g.co/kgs/zBo59R
Constantin L.
"Best decision of my life, great experience, absolutely the best staff in health care, learned more about my injury than I would’ve dreamed of and got to know people that have gone through the same hardship as me, very helpful! If you’ve been suffering with PCS, think no further!"
Review Source:
https://g.co/kgs/hYv6uo
Stacy B.
"I found this clinic during an online search of my symptoms. These guys are the first people to have ever taken me seriously and are some of the kindest human beings I have ever met. The program is extremely intensive and while I have not recovered fully yet, I feel like I have hope for the first time in 5 years. They give you a customized program to follow when you go home and I hopeful that by following this I will continue to improve. If you are struggling with brain function issues, please give them a shot - they are expensive but truly the best of the best."
Review Source:
https://g.co/kgs/SwJYMW
Hannah N.
"This therapy treatment program was a lot of work but after just my first 2 days I had already seen so many positive impacts in my health. My body started to begin functioning like it did before my concussion. Everyone was very helpful and patient with me. I also loved that all the treatments were catered to my physical needs everyday."
Review Source:
https://g.co/kgs/uLhW6G
Michelle B
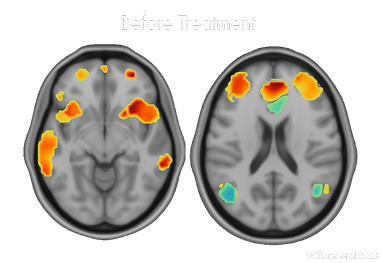
I cannot rate Cognitive FX highly enough! Their accelerated TMS treatment proved to be incredibly effective with clear results. The staff were approachable and friendly, happy to assist in any way possible, making sure my every comfort and need were being met. They were careful to collect all the fMRIs and other information they needed before starting treatment. The treatment itself took five, eight-hour days and I had a reliable schedule created for me, treatments intermittent with exercise, therapy, massage sessions, and time just to relax and take a break. Food was provided for lunches as well as snacks any time I wanted. The accelerated TMS, while not a comfortable treatment, was made better by the staff taking feedback and adjusting the machine accordingly and entertaining me through each ten minute session. This treatment and facility went above and beyond my expectations. Cognitive FX turned out to be the miracle I needed and it's my hope that more places like Cognitive FX will make this treatment accessible to anyone who needs it.
Review Source:
https://g.co/kgs/2onAArP
How ONE-D TMS is different from rTMS and SAINT TMS
1. How long does ONE-D TMS take compared to the different treatment options?
Conventional repetitive TMS (rTMS) is a proven treatment, but it is often logistically burdensome, requiring dozens of clinic visits over four to six weeks. The ONE-D protocol is a breakthrough designed to eliminate this barrier by condensing the entire course of therapy into a single, 9.5-hour day (20 sessions delivered every 30 minutes). This accelerated regimen makes effective treatment feasible for patients who live far from a clinic, have mobility issues, or cannot take weeks off work for daily appointments. SNT TMS is basically the ONE-D TMS protocol that is repeated for 5 days instead of one.
2. How does ONE-D differ from other accelerated protocols like SAINT TMS?
-
Duration: ONE-D is a single-day (9.5-hour) treatment, whereas SAINT (Stanford Accelerated Intelligent Neuromodulation Therapy) is typically a 5-day course.
-
Targeting: SAINT uses personalized targeting via functional MRI (fMRI) to locate the exact stimulation site. ONE-D uses a validated, scalp-based heuristic target for the left posterior DLPFC, making the procedure more accessible and faster to set up.
-
Response Onset: A key finding of the ONE-D study was a delayed therapeutic response, with symptom improvement steadily increasing and reaching a plateau between weeks 4 and 6 post-treatment. This contrasts with the SAINT protocol, which reported a much more rapid response, with remission achieved in an average of 2.6 days.
- SAINT, via a Magnus Medical machine, is an FDA-approved treatment. ONE-D uses FDA-approved iTBS but is still considered off-label.
3. What is "Neuroplastogen Enhancement," and is it unique to ONE-D?
The "Neuroplastogen-Enhanced" element is central to the ONE-D protocol's ability to achieve high results in a single day. ONE-D is optimized by administering a single pre-treatment dose of two off-label medications, D-cycloserine (DCS) and lisdexamfetamine, about an hour before starting TMS. These agents are included to enhance neuroplasticity—the brain's ability to create new connections—which may increase the treatment's effect and durability. Conventional rTMS and SAINT TMS typically do not include this type of pharmacological augmentation.
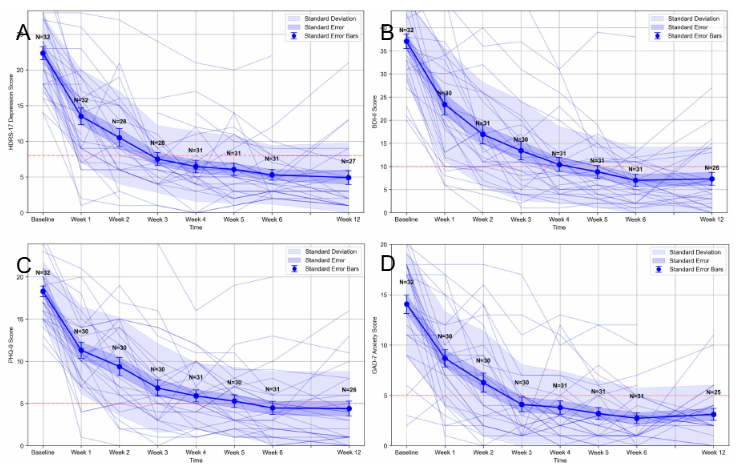
4. How effective is the ONE-D single-day treatment compared to the multi-week options?
The retrospective case series found that the ONE-D regimen achieved unexpectedly high and sustained efficacy despite its brevity and non-personalized targeting. At Week 6 post-treatment, patients achieved:
-
Response Rates: Approximately 88% across depression (HDRS-17, PHQ-9) and anxiety (GAD-7) scales.
-
Remission Rates: Over 70% on the main depression scales (HDRS-17, BDI-II).
- The main question that remains is how durable the recovery is and how often follow-up care is needed.
5. Is the ONE-D protocol safe, and are the results long-lasting?
The ONE-D regimen was found to be safe and well-tolerated, with every patient successfully completing the full 20 sessions on schedule and no serious adverse events reported. The most common side effect was transient scalp discomfort and headache during or in the week following treatment, which is common with TMS. The high response and remission rates were largely maintained out to 12 weeks of follow-up, suggesting the benefit is durable. The study's authors note that a single-day treatment, if replicated under formal randomized conditions, could substantially increase the overall value of TMS as a practical treatment option.
6. Is ONE-D TMS covered by insurance?
Given that the protocol is so new, most insurance plans do not yet cover the treatment. We currently offer it on a cash basis or can try to arrange a single case treatment agreement with your existing insurance. The single case agreement is most effective if you have already met your deductible, given the $2500 cost of the scan plus treatment is generally below most deductibles.