CLICK ANY PART OF THE BRAIN TO LEARN MORE
How EPIC Treatment Will Help You Recover




Enhanced Performance in Cognition (EPIC) Treatment is our 1-2 week treatment program designed to effectively treat post-concussion syndrome and symptoms. Based on your fNCI brain scan, our therapist with adjust their therapies to address your symptoms and work to heal your brain.





What Is PCS?
Post-Concussion Symptoms
Suffering from post-concussion syndrome or symptoms (PCS), is far too common. PCS is when concussion symptoms continue for months or years after an initial concussion or brain injury. Because of the complexity of treating PCS, most patients are put through minimally effective treatments by their doctors. After years of "trial and error,” patients often lose hope for significant recovery.
Because the brain directs the body, an individual's symptoms could easily be attributed to something other than their concussion or mild Traumatic Brain Injury (mTBI). As reported by our patients, most of their doctors seemed to treat everything other than the root cause of their symptoms - their brain.
PCS can impact all areas of life. We organize symptoms into four different categories: Emotional, Physical, Cognitive, and Sleep. Emotional symptoms can include depression and anxiety and can easily be confused with other mental health conditions. Physical symptoms can include headaches, vision changes, light or noise sensitivity. Cognitive symptoms include memory problems, brain fog, finding the right words, and difficulty focusing. Sleep can be impacted by sleeping too much, too little, or being unable to fall asleep.
At Cognitive FX, we know that treating and recovering from PCS is possible with the right diagnostic tools and an understanding of how to apply those findings to treatment and therapies.
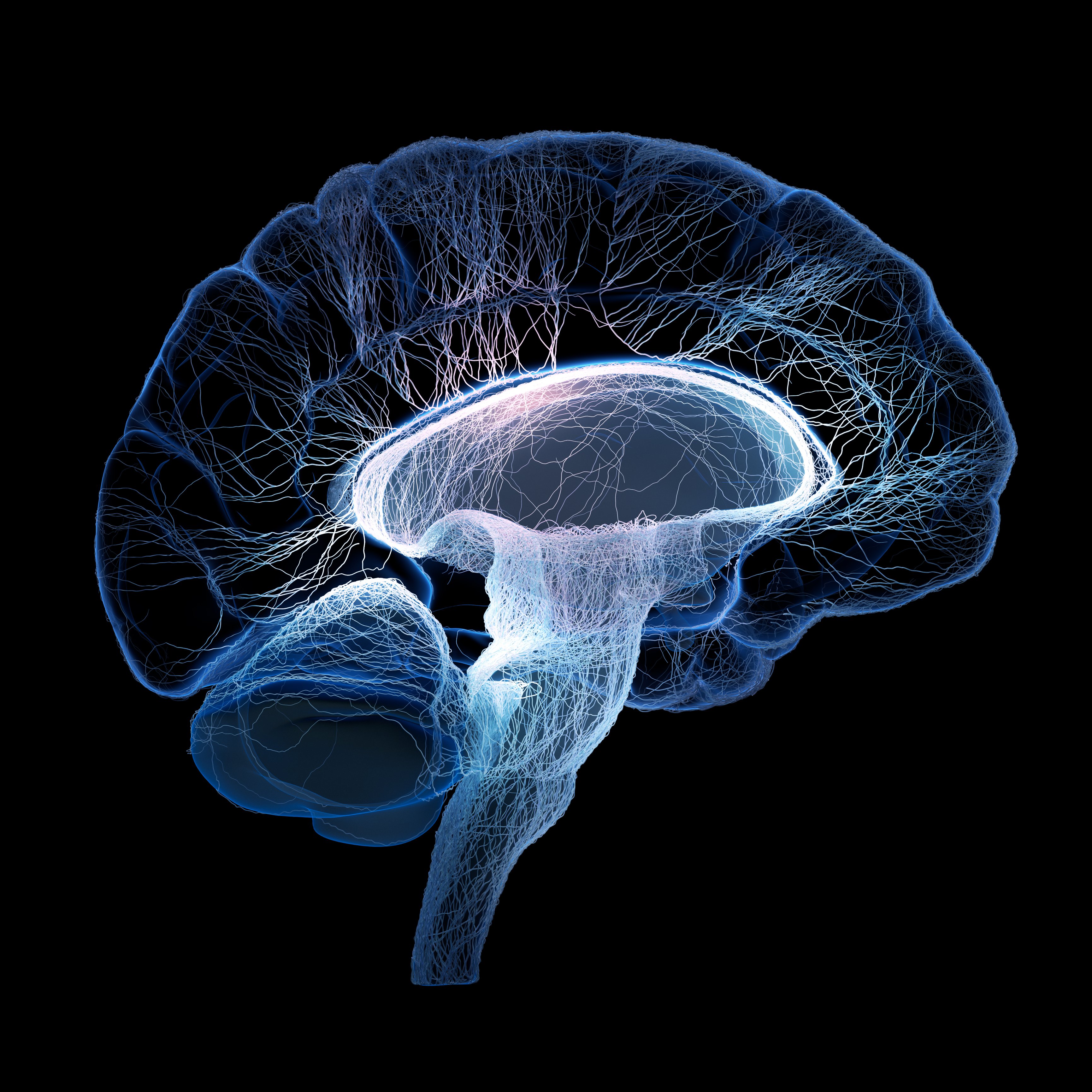
How a Concussion Affects the Brain
BRAINSTEM
Brainstem
The brainstem is made up of the midbrain, medulla, and pons. This part of the brain connects the other parts of the brain to the spinal cord. The brainstem is responsible for maintaining your vitals like heart rate, breathing, and body temperature. It also contributes to other functions like sneezing, coughing, and swallowing.
Concussion Symptoms: In a concussion caused by a sudden head twist, the brainstem can be temporarily separated from the spinal cord, which can effectively sever the corpus callosum (the connective tissues between the right and left hemispheres of the brain). The portion of the brainstem that controls lens focusing within our eyes can be damaged in a concussion, resulting in vision impairment. After a concussion, injury to the brain stem can also contribute to nausea.
CEREBELLUM
Cerebellum
The cerebellum is the part of the brain directly under the cerebrum. The primary responsibility of this part of the brain is to help coordinate muscles and maintain balance. Your cerebellum helps with your posture.
Concussion Symptoms: A concussion that damages the cerebellum can result in: Uncoordinated and slow movements, Dizziness, Loss of balance , Tendency to fall, Slight tremors, Inability to perform rapid movements, or Slurred speech
TEMPORAL LOBE
Located in the Cerebrum
The temporal lobe, like the parietal lobe, helps us understand what we hear, and, therefore, aids our understanding and interpretation of language. It helps us to retain information and interpret sound. The temporal lobe also contributes to our ability to organize information.
Concussion Symptoms: The temporal lobe is a highly vulnerable area of the brain. Damages to the temporal lobe due to closed-head injuries like concussions can result in: Sensitivity to sounds; Impaired ability to hear and comprehend language; Changes to short and long-term memory; Difficulty remembering words, people, things, names, past experiences and more; Trouble getting good sleep; or Possibly seizures.
OCCIPITAL LOBE
Located in the Cerebrum
The primary responsibility of the occipital lobe is to help us interpret what we see. It helps us convert the image our eyes see into colors, light, and movement.
Concussion Symptoms: Damage to the occipital lobe can cause: Sensitivity to light, Loss of vision and/or hallucinations, Double vision, or Difficulty seeing nearby objects.
PARIETAL LOBE
Located in the Cerebrum
The parietal lobe helps us move and determines our orientation in space.. It is also responsible for depth perception, connecting the senses, and processing stimuli.
Concussion Symptoms: If damage is caused to the parietal lobe after a concussion, a patient will likely experience: Difficulty reading, or frequently losing their place; Impairment of the ability to find things; Hard time distinguishing left from right, making it hard to follow navigation and get from one location to the next; Clumsiness; or Struggling to recognize where their body is in location to objects around them.
FRONTAL LOBE
Located in the Cerebrum
The frontal lobe in the cerebrum contributes most to your personality. We rely on this section of the brain to determine our behavior, emotions, and rational thinking or executive function. The frontal lobe also helps regulate body movement and contributes to our ability to write and speak.
Concussion Symptoms: The frontal lobe is one of the most vulnerable areas of the brain due to its proximity to the skull. A concussion can affect the frontal lobe by: Impairing judgment, Impacting attention span and organization, Loss of motivation, Irrational or impulsive behavior, Depression and anxiety, Confusion, Brain fog, Poor concentration, Headaches
How a Concussion Affects the Brain
CLICK ANY PART OF THE BRAIN TO LEARN MORE
Click a different part of the brain in order to determine the effect a concussion can have on each part.
BRAINSTEM
![]() Brainstem
Brainstem
The brainstem is made up of the midbrain, medulla, and pons. This part of the brain connects the other parts of the brain to the spinal cord. The brainstem is responsible for maintaining your vitals like heart rate, breathing, and body temperature. It also contributes to other functions like sneezing, coughing, and swallowing.
Concussion Symptoms: In a concussion caused by a sudden head twist, the brainstem can be temporarily separated from the spinal cord, which can effectively sever the corpus callosum (the connective tissues between the right and left hemispheres of the brain). The portion of the brainstem that controls lens focusing within our eyes can be damaged in a concussion, resulting in vision impairment. After a concussion, injury to the brain stem can also contribute to nausea.
CEREBELLUM
![]() Cerebellum
Cerebellum
The cerebellum is the part of the brain directly under the cerebrum. The primary responsibility of this part of the brain is to help coordinate muscles and maintain balance. Your cerebellum helps with your posture.
Concussion Symptoms: A concussion that damages the cerebellum can result in: Uncoordinated and slow movements, Dizziness, Loss of balance , Tendency to fall, Slight tremors, Inability to perform rapid movements, or Slurred speech
TEMPORAL LOBE
![]() Located in the Cerebrum
Located in the Cerebrum
The temporal lobe, like the parietal lobe, helps us understand what we hear, and, therefore, aids our understanding and interpretation of language. It helps us to retain information and interpret sound. The temporal lobe also contributes to our ability to organize information.
Concussion Symptoms: The temporal lobe is a highly vulnerable area of the brain. Damages to the temporal lobe due to closed-head injuries like concussions can result in: Sensitivity to sounds; Impaired ability to hear and comprehend language; Changes to short and long-term memory; Difficulty remembering words, people, things, names, past experiences and more; Trouble getting good sleep; or Possibly seizures.
OCCIPITAL LOBE
![]() Located in the Cerebrum
Located in the Cerebrum
The primary responsibility of the occipital lobe is to help us interpret what we see. It helps us convert the image our eyes see into colors, light, and movement.
Concussion Symptoms: Damage to the occipital lobe can cause: Sensitivity to light, Loss of vision and/or hallucinations, Double vision, or Difficulty seeing nearby objects.
PARIETAL LOBE
![]() Located in the Cerebrum
Located in the Cerebrum
The parietal lobe helps us move and determines our orientation in space.. It is also responsible for depth perception, connecting the senses, and processing stimuli.
Concussion Symptoms: If damage is caused to the parietal lobe after a concussion, a patient will likely experience: Difficulty reading, or frequently losing their place; Impairment of the ability to find things; Hard time distinguishing left from right, making it hard to follow navigation and get from one location to the next; Clumsiness; or Struggling to recognize where their body is in location to objects around them.
FRONTAL LOBE
![]() Located in the Cerebrum
Located in the Cerebrum
The frontal lobe in the cerebrum contributes most to your personality. We rely on this section of the brain to determine our behavior, emotions, and rational thinking or executive function. The frontal lobe also helps regulate body movement and contributes to our ability to write and speak.
Concussion Symptoms: The frontal lobe is one of the most vulnerable areas of the brain due to its proximity to the skull. A concussion can affect the frontal lobe by: Impairing judgment, Impacting attention span and organization, Loss of motivation, Irrational or impulsive behavior, Depression and anxiety, Confusion, Brain fog, Poor concentration, Headaches
Why Treatment Works
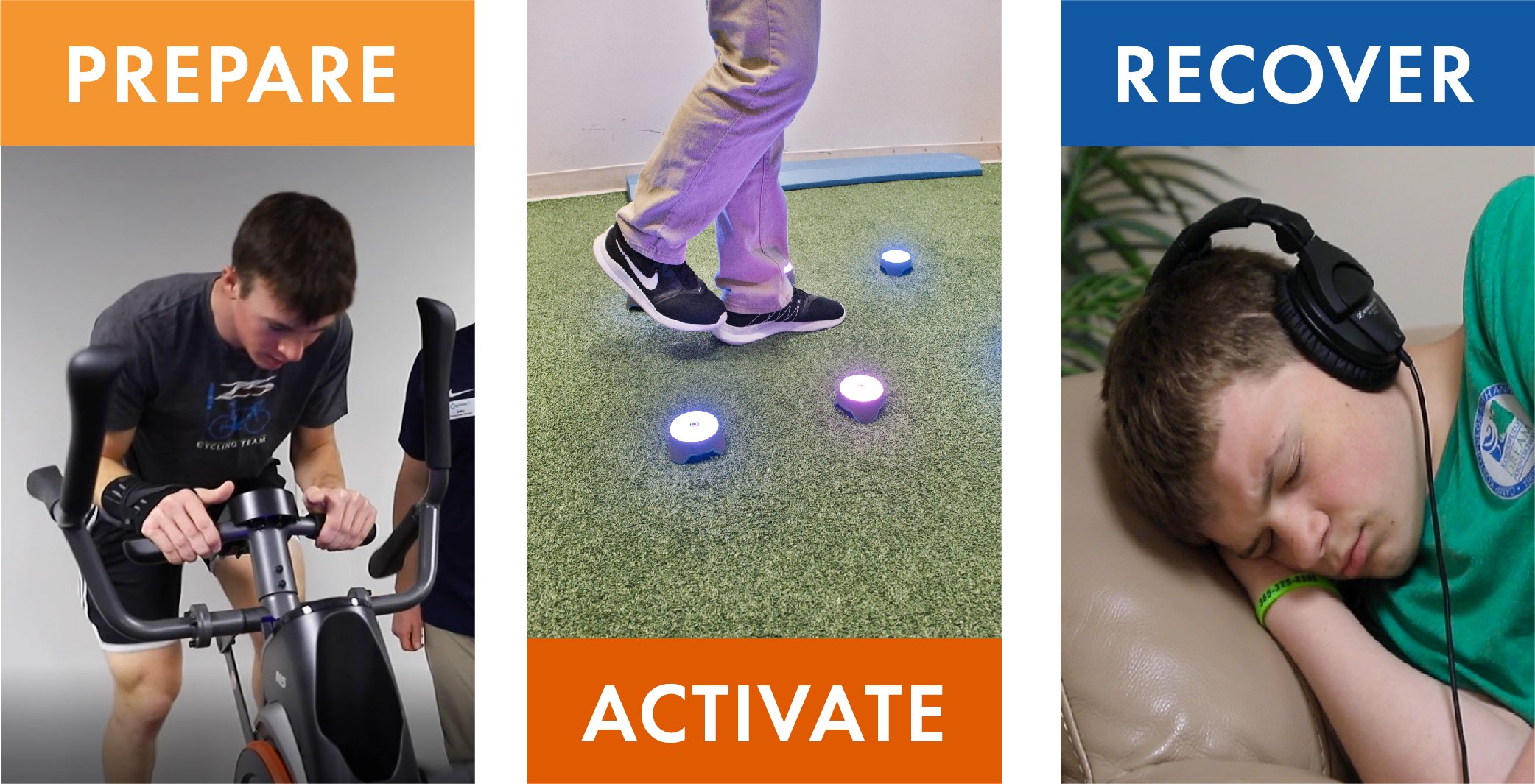
The Prepare-Activate-Rest Cycle is a crucial aspect of the Treatment at Cognitive FX. This cycle dictates your treatment schedule and is a big reason why one or two weeks of treatment produce the amazing treatment results our patients see.
Prepare
The prepare stage is exactly what it sounds like: It prepares your brain for cognitive activity. Our neuromuscular therapists help you prepare for cognitive activity by doing physical exercise with you.
Exercise improves blood flow to the brain and provides neurotrophins and other neurochemicals the brain needs to function properly.
Activate
The activate phase includes the many therapies we do at Cognitive FX which aim to stimulate and regulate those regions of your brain that are not functioning properly. This includes cognitive, multi-sensory, visual, and vestibular activities.
During each of these activities, therapist will use your fNCI report to target specific brain regions and help improve overall functioning.
Recover
The recovery phase is a crucial component of brain injury recovery. At Cognitive FX we help our patients rest and destimulate by using techniques such as brainwaves, mindful breathing, or massage.