How Much Does TMS for Depression Cost?
The type of protocol used is the most important factor influencing the price of TMS. Conventional TMS protocols are often the most affordable, while advanced protocols typically cost more, but can...

If you suffer from major depression, obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), or other mental health conditions, transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) has been proven to help. You may want to explore whether TMS is the right treatment for you.
Are you a good candidate for TMS therapy? What factors should you consider when determining this?
In this article, we’ll discuss these factors, focusing on the latest and most effective TMS protocol: Stanford Accelerated Intelligent Neuromodulation Therapy (SAINT™).
Below, we cover:
SAINT™ TMS, also called the SAINT protocol, is a new TMS method FDA-approved for treatment-resistant depression in 2022.
Several characteristics separate SAINT™ TMS from the original form of TMS (repetitive TMS or rTMS):
In 2018, the FDA approved a new version of accelerated TMS called Intermittent Theta-Burst Stimulation (iTBS). This method uses theta waves, the neural frequencies that the hippocampus uses to connect to other brain regions, form new memories, and regulate certain sleep phases.
This method is safe and effective; many patients experience improvements shortly after starting treatment. It is delivered in three-minute sessions instead of the ~40-minute sessions of rTMS. In addition, patients have also noticed a decrease in suicidal ideation, suggesting that iTBS could be an option to treat patients at high risk of suicide rapidly.
In the standard rTMS and iTBS protocols, the location to apply the magnetic coil (which delivers the brain stimulation) is calculated based on triangulation between the patient’s nose, ears, and top of the head. Coil placement involves measuring the scalp 5cm along the parasagittal plane anterior to the activation hotspot in the motor cortex.
This method is easy to implement and requires no further equipment, but it doesn’t account for variations in head size and shape or differences in brain organization between patients. In addition, it relies heavily on how well technicians can find the right spot.
This can significantly impact the overall treatment results, as even missing it by a few millimeters can lower the treatment’s effectiveness.
A much more accurate way involves using functional MRI to determine exactly where the treatment target area is located in the brain. This method, developed by the team at Stanford University, is a defining characteristic of the SAINT™ protocol.
The SAINT™ protocol uses a technology called “neuronavigation” to ensure that the magnetic coil is placed over the exact spot on the patient's head that the fMRI identified as the target area for each treatment session. This is in contrast to standard TMS in which the magnetic coil is placed manually by clinicians during each treatment session, leading to variability in coil placement from session to session.
In contrast to rTMS, which requires four to six weeks of treatment, with ~40-minute sessions five days per week, SAINT TMS offers a more efficient one-week treatment plan. Patients sit for 10 three-minute iTBS sessions daily for five days, making it much more convenient for people to complete amidst work, childcare, and other life commitments.
SAINT TMS is now considered the gold standard treatment option for treatment-resistant depression.
In a double-blind randomized controlled clinical trial, about 85.7% of patients responded to the SAINT™ treatment, meeting the criteria for reduced symptoms of depression, while around 78.6% achieved remission. All participants had treatment-resistant depression and had failed at least two other depression treatments. Encouragingly, one month after treatment, 60% of patients remained in remission.
The rapid achievement of high response and remission rates with SAINT™, combined with minimal side effects, makes it one of the most effective treatments available today.
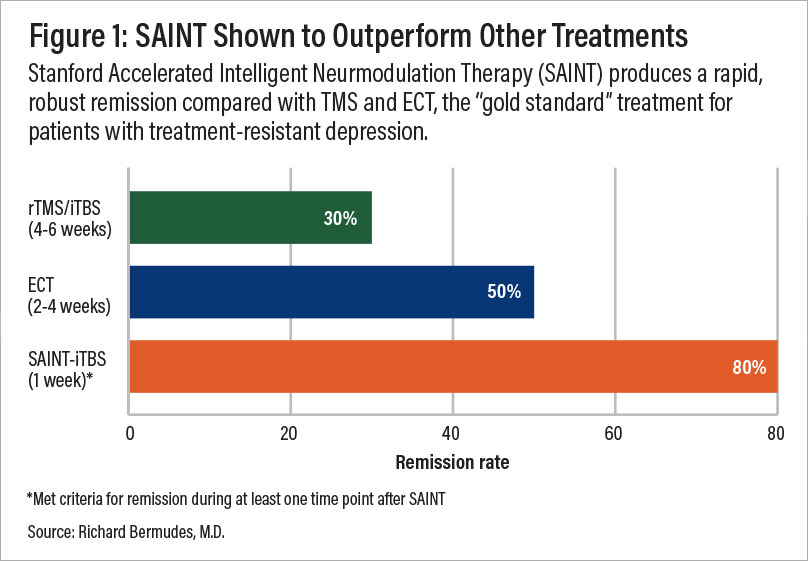
A comparison of remission rates for rTMS/iTBS, electroconvulsive therapy (ECT), and SAINT-iTBS.
The speed with which SAINT TMS can achieve high response and remission rates, combined with minimal side effects, makes it one of the best fact-acting treatments available today. With that said, there is limited data on the durability of these outcomes and how well they hold up over time. Some patients may see lasting remission or symptom reduction, while others may need follow-up treatments to maintain effectiveness.
As such, combining TMS with CBT, as we do at our clinic, is likely to produce the best results for patients. SAINT TMS can be used to get quick relief, while CBT can support long-term outcomes.
As mentioned above, SAINT™ TMS is currently FDA-approved as a new treatment option for major depressive disorder (MDD). In particular, if you have treatment-resistant depression (TRD) — i.e. multiple types of antidepressant medications or other depression treatments have failed to work for you — you’re likely a good candidate for SAINT TMS.
If antidepressant medications haven’t worked for you, you’re not alone. A 2022 reanalysis of the largest antidepressant study ever conducted found that traditional antidepressant medications only relieve symptoms in about one-third of patients who take them.
The study also showed that trying more than two different antidepressant medications brings little benefit for the patients, and less than 2% experienced success with a third or fourth medication.
If you fall into the two-thirds of people for whom antidepressant medications have no effect, this is a sign you may be a good fit for SAINT TMS (and TMS in general).
When taking antidepressant medication, many patients experience side effects, such as insomnia, headaches, nausea, blurred vision, irritability, anxiety, and irregular heartbeat. Most of these are mild and eventually go away, but others can be serious and have severe long-term consequences. For example, studies have shown that long-term use of antidepressant medication can increase your risk of certain illnesses, such as type 2 diabetes.
If you’re struggling to cope with side effects from your antidepressant medication, SAINT TMS is certainly a better option for you. This treatment is associated with only mild and short-lived side effects. Mild headaches and scalp discomfort are the most common side effects after a TMS session, but these symptoms often disappear after the initial sessions.
The most serious potential side effects of TMS are seizures, but these are very rare. Estimates suggest that fewer than three patients experience a seizure per 100,000 sessions. Even for patients who experience a seizure during treatment, it has no serious long-term consequences. There is no evidence that patients can experience multiple seizures during TMS sessions.
In less than 1% of cases, patients report unexpected emotional responses, including exaggerated mood swings and manic episodes. These occur especially in patients with bipolar disorder and taking antidepressant medication. In all cases, these psychiatric changes subsided shortly after treatment.
If you’ve tried rTMS and failed to see any improvement, you may be reluctant to try TMS again. However, it is possible that your first TMS treatment failed because the method of placing the coil was imprecise or inconsistent.
As discussed above, SAINT TMS solves this issue. Using fMRI and neuronavigation ensures that the correct brain region is properly stimulated in nearly all patients, while simpler methods that rely on measurements taken over the patient’s scalp are successful in less than half.
Depression can cause serious and debilitating symptoms that can affect daily life, including thinking about self-harm and suicide. Standard treatments such as antidepressant medication (which may actually increase suicidal thoughts) and talk therapy take weeks or months to begin working.
In contrast, TMS is a rapid and safe way to relieve depressive symptoms, including suicidal ideation. More than other types of TMS, SAINT has been shown to rapidly reduce the severity of suicidal ideation in just five days. There is some evidence that patients with suicidal ideation often have damage to areas of the brain that are involved in cognitive and emotional control, which happen to be the areas targeted during TMS sessions.
Many people simply do not have the time to participate in 40-minute treatment sessions five days per week for four to six weeks. If this is the case for you, and you’re otherwise a good fit for TMS, SAINT TMS or another form of accelerated TMS is a good option for you.
Most patients can safely undergo a TMS treatment, but some situations may rule out patients from TMS sessions. In most cases, it is a matter of assessing whether the increased risk outweighs the potential benefits. If these conditions apply to your medical history, our best advice is to discuss it with your healthcare provider.
TMS may not be possible for you if you have a metallic implant (or other objects) in the brain close to where the coil needs to be placed. This includes, for example, cochlear implants, Internal Pulse Generators, medication pumps, aneurysm clips or coils, stents, or even bullet fragments. Braces and dental fillings are acceptable for treatment.
Patients with these cannot undergo TMS because the magnetic fields could malfunction the implanted devices. Under normal circumstances, the heating produced during a TMS session is negligible and poses no risk to the patient. However, TMS can overheat metal objects and cause irreversible damage to the brain. Low-conductivity plastic and titanium implants are less prone to heating up.
If you have a history of seizures, TMS may also not be right for you. Although rare, seizures can occur during TMS sessions and are more likely in patients with a previous history of seizures or suffering from neuropsychiatric diseases, including epilepsy, multiple sclerosis, traumatic brain injury, and Alzheimer’s disease, to name just a few.
The best way to minimize the risk of experiencing a seizure is to look at all factors that may increase your risk of seizures, such as prescription medication and history of seizures. In conjunction with your healthcare provider, you can weigh the pros and cons and decide whether TMS is suitable for you.
TMS may not be suitable for you if you’re already taking prescription drugs known to increase the risk of seizures. Although there is no evidence to suggest an increased risk of seizures beyond the risk already associated with TMS, if you’re currently on medication, it is important to discuss it with your healthcare professional before starting TMS. Your doctor may decide that you can undergo TMS sessions, but you may need to be followed more closely during your treatment.
At Cognitive FX, we are currently not treating patients younger than 16 and older than 65 for safety reasons. Preliminary studies show that TMS is likely safe for these patients, but further research is needed.
Beyond medical factors, some patients may also face practical barriers to treatment, such as insurance coverage limitations, cost, or geographical constraints. If these apply to you, discussing alternative options with your provider may help you explore solutions.
While SAINT offers significant advantages over traditional TMS, the following may make it less accessible:
Lack of insurance coverage: Most insurance plans do not yet cover SAINT, as it is a newer protocol compared to standard TMS. However, coverage policies vary, so it’s important to check with your insurance provider to confirm your options. The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) have announced that hospitals will be reimbursed $19,703 for the full SAINT protocol, beginning July 1, 2025.
High treatment costs: Currently, SAINT TMS treatments typically range from $30,000 to $36,000, making the cost a significant barrier for many patients. There are, however, close alternatives available at a significantly lower price (discussed below).
Limited availability: Fewer than 10 clinics in the U.S. currently offer SAINT, with most providers still using rTMS. However, more clinics are beginning to adopt accelerated TMS and intermittent theta burst stimulation (iTBS) protocols, signaling a gradual shift toward newer treatment methods.
If you’re considering SAINT™, discussing financial and logistical concerns with your provider can help you explore potential solutions, such as financing options or alternative treatment locations.
Our clinic, based in Provo, Utah, provides an alternative to SAINT™ TMS that offers the same precision of personalized treatment targeting, combined with FDA-approved theta burst stimulation at a significantly lower cost. This approach delivers the same core elements that make SAINT™ so revolutionary.
The only difference between our treatment and SAINT™ (a trademark licensed to Stanford Medical) is our targeting method. Our target locations are determined by fMRI and our prescribing neuroscientist and physician, rather than their proprietary software.
| Accelerated fMRI - TMS | Magnus SAINT™ TMS | |
|---|---|---|
| FDA-Approved iTBS | ✔ | ✔ |
| FDA-Approved Neuronavigators | ✔ | ✔ |
| FDA-Approved Figure 8 Coils | ✔ | ✔ |
| Number of Treatment Days | 5 | 5 |
| Treatments per Day | 10 | 10 |
| Total Treatments | 50 | 50 |
| Number of TMS Pulses | Approx. 90,000 | 90,000 |
| Resting motor threshold pulse intensity | 90–120% | 90–120% |
| FDA-Approved Personalized DLPFC Targeting | ✘ | ✔ |
| Personalized DLPFC Targeting Assists Doctor in Target Location | ✔ | ✘ |
| Personalized E Field Coil orientation | ✔ | ✘ |
| Cost | $9,000 to $12,000 | $30,000+ |
As we’ve highlighted throughout this article, this protocol of TMS is:
Safe: Widely tolerated and associated with mild, short-lasting side effects.
Precise: fMRI ensures that the treatment target area is precisely located for each patient, accounting for variations in head size and shape. Neuronavigation ensures the magnetic coil is placed over that exact spot for every treatment session.
Fast: Treatment courses are reduced to a single week, making it easier to complete alongside life and work commitments (compared to 4 to 6 weeks of standard TMS and accelerated TMS protocols).
Effective: Precision coil placement combined with theta burst stimulation produces the best TMS treatment results to date.
To improve outcomes for our patients, we also include cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) as a part of our treatment. When combined with the traditional method of TMS (rTMS), CBT improved response and remission rates by ~8% and ~19%, respectively. Additionally, CBT is likely to produce sustained improvement over time once treatment has concluded.
Our brain stimulation treatment is ideal for most patients with treatment-resistant depression. However, we do not treat patients under the age of 18 or over 65. Additionally, as a safety measure, we do not treat patients who have a history of seizures or who are currently actively suicidal and in need of crisis care.
Click here to learn more about receiving accelerated fMRI TMS therapy at Cognitive FX.

Dr. Mark D. Allen holds a Ph.D. in Cognitive Science from Johns Hopkins University and received post-doctoral training in Cognitive Neuroscience and Functional Neuroimaging at the University of Washington. As a co-founder of Cognitive Fx, he played a pivotal role in establishing the unique and exceptional treatment approach. Dr. Allen is renowned for his pioneering work in adapting fMRI for clinical use. His contributions encompass neuroimaging biomarkers development for post-concussion diagnosis and innovative research into the pathophysiology of chronic post-concussion symptoms. He's conducted over 10,000 individualized fMRI patient assessments and crafted a high-intensity interval training program for neuronal and cerebrovascular recovery. Dr. Allen has also co-engineered a machine learning-based neuroanatomical discovery tool and advanced fMRI analysis techniques, ensuring more reliable analysis for concussion patients.

The type of protocol used is the most important factor influencing the price of TMS. Conventional TMS protocols are often the most affordable, while advanced protocols typically cost more, but can...

Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) and neurofeedback are gaining popularity as non-invasive, medication-free options for treating depression—especially for people who haven’t found relief from ...

A major challenge for patients with depression is that traditional antidepressant medications often take weeks or months to show results — if they work at all. This delay can be especially...
If you’re considering accelerated Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) therapy, it’s important to understand how it works, what to expect, and whether it’s the right fit for you.

Over the past few years, Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) has become an increasingly popular treatment option for patients who haven’t found symptom relief from antidepressant medications.

If you’re considering transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) therapy, it’s essential to understand the potential pros and cons of the treatment. Fortunately, for those suffering from major...