Medication for Post-Concussion Syndrome: Does It Work?
Many doctors aren’t aware that concussions can cause long-lasting symptoms, a condition commonly called post-concussion syndrome (PCS). As a result, they treat common symptoms rather than the...
Published peer-reviewed research shows that Cognitive FX treatment leads to meaningful symptom reduction in post-concussion symptoms for 77% of study participants. Cognitive FX is the only PCS clinic with third-party validated treatment outcomes.
READ FULL STUDY
The type of head injury doctor you need to see depends on the type of injury you’ve experienced and how long ago the injury occurred. Doctors who excel at concussion treatment, for example, are often not the doctors you would see for a skull fracture.
In many cases, you’ll need to see multiple doctors for different aspects of your evaluation. Certain doctors are best for initial injury assessment and healthcare coordination; others are only involved in testing; still others specialize in rehabilitation.
At our treatment clinic, CognitiveFX, our team specializes in neuroimaging and rehabilitation for persistent head injury symptoms; we wouldn’t be the place to go the day you’re injured.
To help you understand which type of doctor to see for your injury, we’ve put together an extensive list of head injury doctors and when to see them. It’s divided into three sections:
We also discuss when to see a doctor for a head injury and how to find the right doctor. If you are showing any signs of severe head trauma, please visit the nearest emergency department or urgent care clinic for immediate medical attention.
At Cognitive FX, we treat patients whose head injury symptoms did not resolve with time and rest. 95% of our patients experience statistically verified restoration of brain function after treatment. To learn if our program is right for you, schedule a consultation.
Note: Any data relating to brain function mentioned in this post is from our first generation fNCI scans. Gen 1 scans compared activation in various regions of the brain with a control database of healthy brains. Our clinic is now rolling out second-generation fNCI which looks both at the activation of individual brain regions and at the connections between brain regions. Results are interpreted and reported differently for Gen 2 than for Gen 1; reports will not look the same if you come into the clinic for treatment.
 Infographic from Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) website.
Infographic from Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) website.
Most of the time, if you hit your head, it’s a good idea to visit a doctor.
If you experience any of these symptoms after hitting your head (or notice them in a family member or friend), consider it a medical emergency:
Surface wounds on your scalp can bleed profusely, so it’s not automatically a sign of serious injury. Nevertheless, it’s best to have your injury examined by a medical professional if your head is bleeding.
What if you hit your head but aren’t exhibiting the signs of a serious injury?
That somewhat depends on how you are feeling and whether you want to play it safe. If you’re experiencing symptoms like a headache, balance problems, foggy thinking, emotional changes, blurred vision, memory loss, or other issues, it is likely that you have a concussion. Working with the right treatment team sooner rather than later can reduce your odds of developing long-term symptoms.
If you choose to wait to see a doctor, keep track of how long it’s been since the injury. If your post-concussion symptoms haven’t resolved after three months or you notice rapidly worsening symptoms, contact our team for a consultation. We’d be happy to advise you on next-steps so you can start feeling better again.
Many different doctors treat head injury, but not all of them treat the same types of injury in the same ways. We’ll explain when you might encounter these doctors and other care providers, along with what they can offer when you visit them.
Here’s a quick peek at the types of doctors covered in the list:

Many people visit a general physician (or, for young children, a pediatric physician) after a suspected concussion. While a general practitioner of medicine can diagnose a concussion, these doctors often do not have the most current information about concussion treatment. Some may then unintentionally offer outdated medical advice (like lying down in a dark room until symptoms resolve) that could increase your chance of developing long-term symptoms. You can read about best practices for concussion treatment here.
Depending on your insurance situation, however, you may need to visit a family physician in order to get a referral to a specialist who can further diagnose and treat your symptoms.
Whether you can get good concussion care from a sports medicine physician depends on their specialty. If their focus is on knee injuries, for example, they may not have the resources you need for concussion recovery. But if they have extensive interest and experience with concussion treatment, they can be a great resource — especially if they have ties to a clinic and can refer you immediately for therapy.
These doctors can provide a sports concussion diagnosis after a physical and cognitive examination. They may test things such as memory, balance, responsiveness and strength. If they have any reason to suspect a more severe injury, they can refer you for a computed tomography scan (CT scan) or magnetic resonance imaging scan (MRI scan).
They can also help you follow a return-to-play protocol to ensure you’re fully recovered before resuming sports and work at normal levels.
Also known as a physiatrist, a PM&R physician who specializes in head injury can help patients with initial concussion diagnosis and treatment or with ongoing care. These physicians can prescribe medication if needed to supplement therapy.
A neurologist may treat a wide range of neurological conditions, such as epilepsy, migraines, degenerative disorders, stroke, and traumatic brain injury. They are well-versed in medication options for brain disorders and might make referrals to other specialists as needed.
Neurologists are a good option to receive an initial diagnosis or treatment referrals, but not all neurologists are the best choice for concussion treatment. Many neurologists never received extensive training in concussion treatment and will turn to medication before other options, even though patients with brain injury are more likely to experience problematic side effects from these medications.
And, if you have persistent symptoms, they may not know how to help: A survey of 289 neurologists showed that the majority did not believe effective treatment was available for persistent symptoms (there is). If you’re curious whether you should visit a neurology practice after concussion, read our post on how a neurologist can help with post-concussion syndrome.
The good news about concussion clinics is that they’re focused on facilitating concussion recovery! The bad news is that some are much better than others. Many clinics do a good job of acute concussion care; however, many do not have effective strategies for handling persistent symptoms (which we’ll discuss later in this post).
How do you know if you’ve found a good clinic? You can use this checklist from our in-depth guide to finding a good concussion clinic:

Note: If you’re in the Salt Lake City or Utah Valley area, we recommend our sister clinic, Neural Effects, for acute concussion care. The sooner you reach out after your concussion, the better they will be able to help you. You can contact their team here.

In most cases, the emergency room will be your first stop for a suspected serious injury. While some people go to the ER for a possible concussion, the most the ER team can do is diagnose your injury and confirm it isn’t more serious.
For severe TBI, the ER doctor will assess your injury, stabilize you if needed, request diagnostic imaging when necessary, and arrange for you to be seen by a specialist — usually a neurosurgeon or a neurologist. While you’re in the ER, doctors and nurses may ask for details about your injury. If you were injured in a car accident, for example, they’ll want to know the speed of the collision, where you were sitting, whether your seatbelt was on, the angle of the car crash, etc. to narrow down the type of brain injury you may have sustained.
If your injury is life-threatening and requires immediate intervention, you’ll be transferred to the intensive care unit (ICU) or an operating room. Patients in a coma will receive a score from the Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS). Doctors will re-assess comatose patients regularly to monitor the progress of the coma.
A neuroradiologist identifies brain injuries via imaging such as CT scans, MRI scans, and even X-rays. They may or may not meet with you directly, but they will definitely be a part of your care anytime your doctor orders a brain scan.
With imaging, they look for brain damage such as hematoma or contusions (bruised and bleeding brain tissue), dead brain cells, and so forth. They’ll also note issues such as skull fracture or blood clots. They may also examine your spinal cord, depending on what type of injury you sustained. If you’re having seizures, they might use a magnetoencephalography (MEG scan) to investigate the cause.
A neurosurgeon can diagnose severe head injuries, order imaging tests, perform surgery, and help you explore alternatives to surgery. Typically, you won’t meet with a neurosurgeon unless another doctor evaluates you and makes the recommendation to see one.
Many people think that neurosurgeons only perform surgery on the brain, but they also treat peripheral nervous system disorders, certain issues with the spine and back, and even carpal tunnel syndrome. And while they do perform surgery when it’s needed, they will help you explore other, less invasive treatment options first.

A neuropsychologist can diagnose cognitive impairment and provide therapy for ongoing symptoms after a head injury. The first step is to determine whether your symptoms stem directly from the injury (or previous injuries) or if they’re due to secondary conditions such as depression, medication, poor sleep quality, and so forth.
During a neuropsychological evaluation, this doctor can assess cognitive skills such as memory, reasoning, and attention using what is known as a paper pencil test. Personality and mood testing can further reveal factors affecting your recovery.
Afterward, a neuropsychologist can work with patients (either directly or via therapists) on lingering issues, plus educate them about what they’re facing and how to cope. You will often meet a neuropsychologist in follow-up appointments designed to assess your progress during a prescribed therapy course.
Therapists are not MDs, but they may have a doctorate in their specialty. Regardless of their educational status, they often play a key role in patient rehabilitation. Some types of therapists who work with head injury patients include:
Which type of therapy you need depends on what symptoms you’re having and specifically where your brain was injured.
Further reading: Brain injury recovery stories from five TBI survivors
While an endocrinologist isn’t a head injury doctor per se, their assistance can be key to recovery. Some patients experience changes in hormone levels following injury. An endocrinologist (or sometimes general practitioners or OB-GYNs) can test your hormone levels and prescribe appropriate treatment.
Try to find one who is accustomed to working with head injury patients. Some specialize in diabetes, for example, which doesn’t always translate to a strong working knowledge of the sometimes unpredictable ways hormones can change after a brain injury.

Up to 30% of concussion patients, along with most TBI patients, suffer from symptoms that do not go away with time. These patients are often told they will just have to live with their symptoms. Others are told their symptoms are made up or unrelated to their brain injury. Some may have received therapy from different specialists, but that therapy doesn’t always work.
There are many reasons for this:
As a result, many patients suffering from lingering head injury symptoms do not receive adequate care. Fortunately, that dynamic is starting to change.
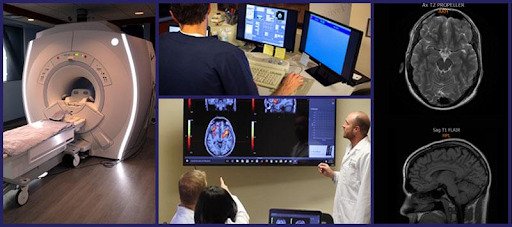
In our published research, we’ve demonstrated that neurovascular coupling (the relationship between neurons and the blood vessels that supply them with oxygen and other micronutrients) underlies lingering concussion symptoms. By using an fNCI scan (a particular way of administering functional MRI, which shows how blood flows through the brain), we can pinpoint which regions of the brain were affected by concussion.
In turn, that knowledge empowers us to treat each unique brain injury with tailored therapy for that patient. We also have a close relationship with a local neurosurgery practice in case our scans discover more serious underlying issues.
Patients at our clinic undergo intense multidisciplinary therapy, including neuromuscular therapy, occupational therapy, cognitive therapy, sensorimotor therapy, neuro integrative therapy, psychotherapy, and more.

Another fNCI scan at the end of treatment confirms patient progress. 95% of our patients experience statistically verified restoration of brain function after treatment at our clinic. Their average one-week improvement on the scan is 75%; average one-week symptom improvement is 60%. We send patients home with additional resources to help them keep improving on their own, and are always available to answer questions.
To learn if you’re eligible for treatment, schedule a consultation with our team.

Alina Fong, Ph.D. is a clinical neuropsychologist and the Clinical Director and Co-Founder of Cognitive FX. She earned her Ph.D. in Clinical Neuropsychology with an emphasis in Neuroimaging from Brigham Young University, where she received the American Psychological Association Division 40 Graduate Student Research Award for her neuroimaging research. Dr. Fong has over 17 years of clinical experience treating traumatic brain injury, beginning with her work at the VA Salt Lake City Healthcare System and Utah Valley Regional Medical Center, where she directed the neurotrauma rehabilitation and sports concussion clinics. She developed the EPIC Treatment protocol and has personally overseen treatment for nearly 8,000 brain injury patients, including professional athletes from the NFL, NHL, and Olympics. She serves as Vice President of the Brain Injury Alliance of Utah, sits on the board of the United States Brain Injury Alliance, and advises PINK Concussions. Dr. Fong has authored peer-reviewed research on functional MRI and concussion treatment and has presented at over 60 medical conferences, including the Federal Interagency Conference on TBI and the American Medical Society for Sports Medicine.

Many doctors aren’t aware that concussions can cause long-lasting symptoms, a condition commonly called post-concussion syndrome (PCS). As a result, they treat common symptoms rather than the...

At our post-concussion treatment clinic, patients sometimes present with short- or long-term hormone dysfunction after brain injury. While we don’t treat hormonal imbalance at our clinic, we often...

Recovering from post-concussion syndrome (PCS) is challenging, but with the right guidance, substantial progress and symptom relief are possible, even years after the initial injury.

Brain injury recovery is hard. The severity of your injury, which parts of your brain were affected, and how they were affected, all factor into things such as how much you can recover and how long...

Neural fatigue can develop after any type of brain injury, including mild traumatic brain injury (concussion), severe traumatic brain injury (TBI), hypoxia,viral infection, stroke, ortransient...

If you’ve been reading about concussion diagnosis and symptoms and feel confused, that’s pretty normal. Most advice about concussions feels vague. It’s hard to know what applies to you. And if you’re...
Published peer-reviewed research shows that Cognitive FX treatment leads to meaningful symptom reduction in post-concussion symptoms for 77% of study participants. Cognitive FX is the only PCS clinic with third-party validated treatment outcomes.
READ FULL STUDY