rTMS vs dTMS for Depression: Which Is Better?
If you’re considering brain stimulation therapy for treating major depression, you may wish to understand the differences between repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) and deep...
Published peer-reviewed research shows that Cognitive FX treatment leads to meaningful symptom reduction in post-concussion symptoms for 77% of study participants. Cognitive FX is the only PCS clinic with third-party validated treatment outcomes.
READ FULL STUDY
If you’re considering brain stimulation therapy for treating major depression, you may wish to understand the differences between repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) and the more recently developed intermittent theta-burst stimulation (iTBS).
This article outlines the key similarities and differences between the two treatments to help patients decide which type is best for them. In addition, it discusses two key limitations of these protocols and explains how Stanford Intelligent Accelerated Neuromodulation Therapy (SAINT™) solves them to provide even better treatment outcomes.
We cover:
The general approaches of iTBS and rTMS protocols are essentially the same. They each involve placing a magnetic coil over a brain region called the left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (L-DLPFC), and delivering magnetic pulses to stimulate neurons in that area, which can help relieve depression symptoms.
Both rTMS and iTBS are characterized by mild, short-term side effects and high tolerability. The most common side effects include headaches and scalp discomfort, which, if needed, can be treated with over-the-counter painkillers. A few patients report hearing problems or dizziness after their TMS session, but this is only temporary.
The most serious adverse event that may result from these treatments is seizures, but the risk is minimal. The risk was slightly higher in the early days of TMS, but additional safety features have been implemented to the procedure, significantly reducing patient risk.
For iTBS, current estimates suggest that less than 3 patients experience a seizure per 100,000 sessions. Seizures are more likely in patients with a history of seizures or suffering from neuropsychiatric diseases, including epilepsy, multiple sclerosis, traumatic brain injury, and Alzheimer’s disease.
Most studies show that the effectiveness of theta burst stimulation is similar to rTMS. Numerous meta-analyses and systematic reviews have shown that rTMS improves symptoms in about 50% of patients with depression, with a remission rate of over 30%. rTMS is particularly effective in patients with mild depressive episodes and non-psychotic depression, and follow-up has shown patients continue to experience the benefits for 6 to 12 months.
Patients who have not responded to multiple antidepressant medications can be more challenging to treat, but ~30% still respond to treatment, and ~19% achieve remission.
When combined with psychotherapy, success rates of rTMS treatment are higher, with remission and response rates of ~55% and ~66%, respectively.
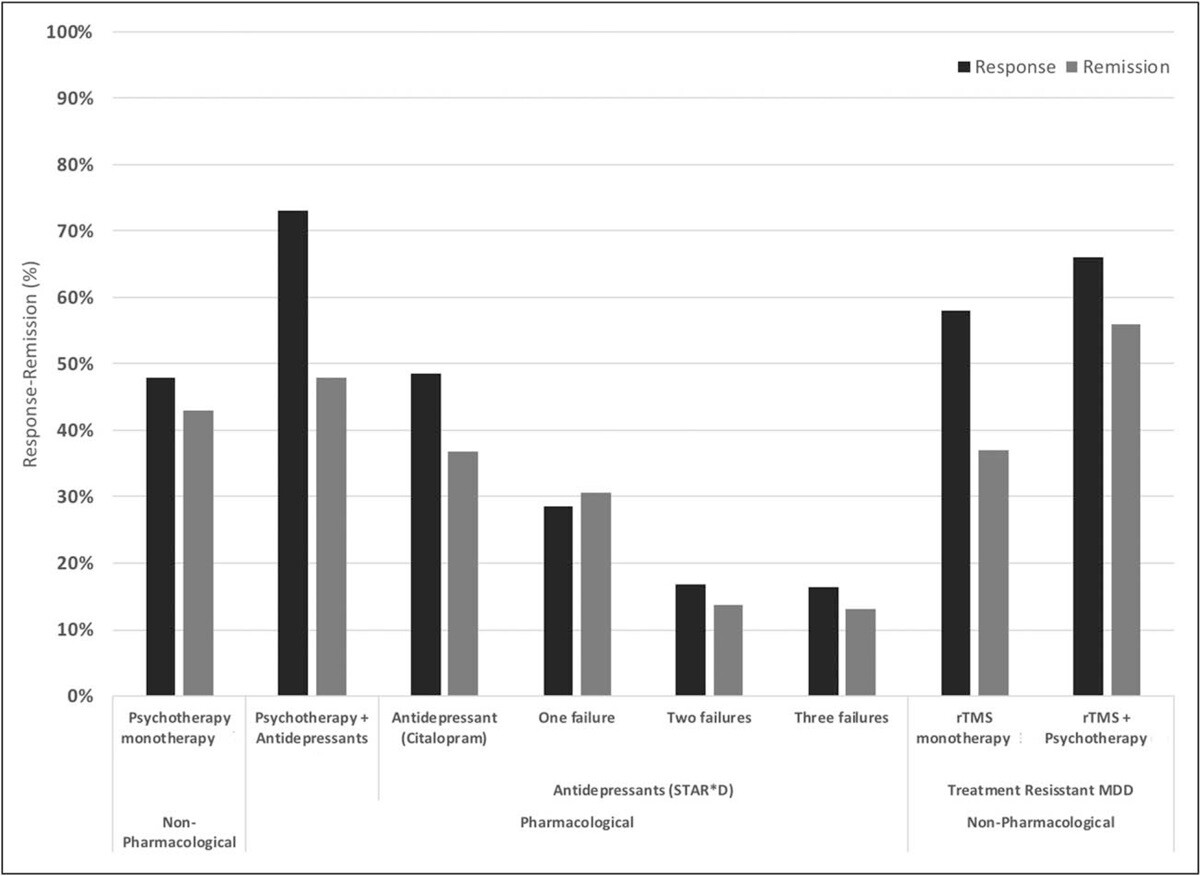
Response and remission rates of various monotherapeutic and combinatory antidepressant treatments based on the largest studies and datasets available. [Source]
iTBS uses a different pulse frequency (the number of pulses delivered per second) and pattern than high-frequency rTMS. The two methods also operate at different percentages of a patient’s resting motor threshold.
With rTMS, individual treatment sessions take ~37 minutes to complete, administered once daily, 5 days per week for 4 to 6 weeks. A major advantage and innovation of iTBS is that sessions can be administered in just 3 minutes, making it much more convenient for patients to get in and out of the clinic throughout the days and weeks they’re undergoing treatment.
Compared to rTMS, some patients receiving iTBS have reportedly noticed a significant decrease in suicidal ideation, suggesting that iTBS could be a better option to rapidly treat patients at high risk of suicide.
In recent years, the number of clinics offering rTMS therapy in the United States has increased significantly. It’s now relatively easy to find a local clinic offering rTMS.
In contrast, clinics offering iTBS are less common because they require newer equipment. For this reason, patients may need to travel to access iTBS treatment. This can add to the overall cost and may be a barrier to care for those with limited mobility or resources.
One of the main advantages of rTMS is widespread coverage by major insurance providers. Most insurance plans, including Medicare and Medicaid, recognize rTMS as an essential treatment for patients with depression and offer partial or full coverage. As such, patients considering rTMS therapy can often rely on their insurance to help make the treatment more affordable.
In contrast, iTBS is not currently covered by insurance companies. In practical terms, this means iTBS is only possible for patients who can cover the costs themselves. A TMS treatment course generally ranges from $6,000 to $15,000 but could be higher in clinics offering specialized technology or additional treatments alongside TMS.
It’s important to note that with rTMS, each insurer may have slightly different criteria for coverage, including specific inclusion criteria like prior failure with medications or psychotherapy. Some insurers specify which types of medications — such as antipsychotics or different classes of antidepressant medication — must be tried first. Additionally, coverage may vary based on the severity of symptoms, with some insurers covering moderate cases while others limit coverage to severe conditions.
Even after receiving insurance approval, patients should expect to pay a copay and/or deductible, which can vary depending on the specific insurance plan. For patients who require further financial assistance, payment plans, healthcare financing, or medical credit cards from companies like CareCredit may be an option.
rTMS and iTBS are both safe and worthwhile depression treatment options to consider, especially with their effectiveness rates and mild side effects compared to most other treatments.
With that said, patients should be aware of the two main limitations of these treatments.
Standard rTMS and iTBS protocols are typically administered with daily sessions, 5 days per week over 4 to 6 weeks — and this lengthy and demanding treatment schedule is often difficult for patients to complete amidst work, childcare, and other life commitments.
It’s also a longer-than-ideal time for patients experiencing severe depression symptoms.
A key aspect of TMS treatment is accurately locating the brain region being targeted and correctly positioning the coil during each session.
In standard rTMS and iTBS protocols, coil placement is typically determined using the "5 cm method," which involves manually measuring distances between the patient’s nose, ears, and the top of the head. However, this approach can be imprecise due to variations in head size, shape, and individual brain structure, which may significantly affect treatment outcomes. Even a miss of the left DLPFC by a few millimeters can reduce the effectiveness of the treatment.
In some cases, an EEG cap is used to help locate the treatment area. While research suggests this method is somewhat more accurate and reliable than the 5 cm method, the difference is minor and not likely to result in substantially improved outcomes. Additionally, factors like a simple haircut can affect how the cap fits, potentially causing variations between sessions.
Stanford Intelligent Accelerated Neuromodulation Therapy (SAINT™), which was FDA-approved to treat major depressive disorder (MDD) in 2022, addresses both of these issues.
First, it uses functional MRI to map brain connectivity and pinpoint the treatment target area for each patient, and neuronavigation to position the magnetic coil directly over the L-DLPFC for every treatment session.
Second, the SAINT protocol condenses treatment into a single week, making it much more convenient for patients to fit into their lives, and offering faster relief. Patients sit for 10 short sessions each day, for 5 days, with a 50-minute break in between sessions.
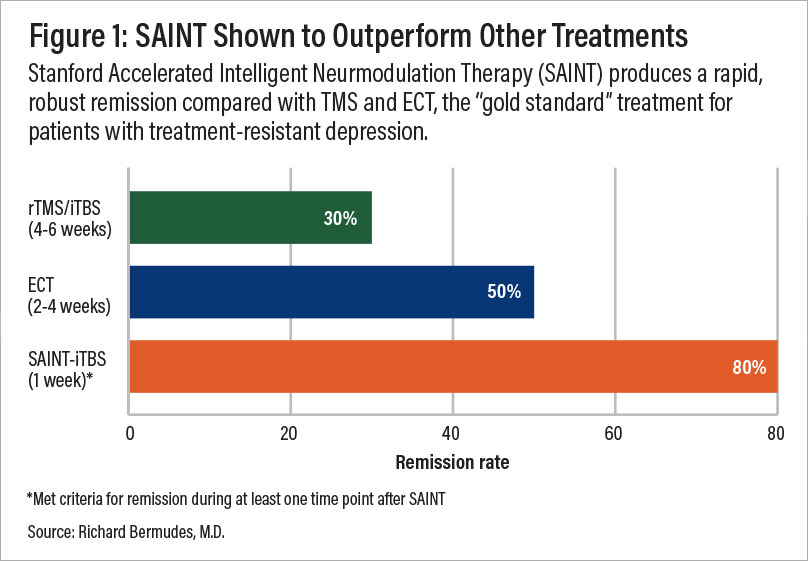
A comparison of remission rates for rTMS/iTBS, electroconvulsive therapy (ECT), and SAINT-iTBS.
Following this protocol significantly reduced depressive symptoms and suicidal ideation within 5 days, without negative side effects. In a double-blind randomized controlled trial, about 85.7% of patients responded to the treatment (meaning they met prespecified criteria for reduced depressive symptoms) and around 78.6% met the remission criterion.
All the individuals in the study had treatment-resistant depression and had failed at least two other depression treatments. One month after the clinical trial, 60% were still in remission. (Find the full text of the sham-controlled study here.)
The speed with which SAINT can achieve high response and remission rates, combined with minimal side effects, makes it one of the best fast-acting depression treatments available today.
With that said, there are some practical barriers that make SAINT treatment less accessible:
Our team at Cognitive FX, based in Provo, Utah, provides an alternative to SAINT TMS that offers the same precision of personalized treatment targeting, combined with FDA-approved theta burst stimulation at a significantly lower cost. This approach delivers the same core elements that make SAINT so revolutionary.
The only difference between our treatment and SAINT (a trademark licensed to Stanford Medical) is our targeting method. Our target locations are determined by fMRI and our prescribing neuroscientist and physician, rather than their proprietary software.
| Accelerated fMRI - TMS | Magnus SAINT™ TMS | |
|---|---|---|
| FDA-Approved iTBS | ✔ | ✔ |
| FDA-Approved Neuronavigators | ✔ | ✔ |
| FDA-Approved Figure 8 Coils | ✔ | ✔ |
| Number of Treatment Days | 5 | 5 |
| Treatments per Day | 10 | 10 |
| Total Treatments | 50 | 50 |
| Number of TMS Pulses | Approx. 90,000 | 90,000 |
| Resting motor threshold pulse intensity | 90–120% | 90–120% |
| FDA-Approved Personalized DLPFC Targeting | ✘ | ✔ |
| Personalized DLPFC Targeting Assists Doctor in Target Location | ✔ | ✘ |
| Personalized E Field Coil orientation | ✔ | ✘ |
| Cost | $9,000 to $12,000 | $30,000+ |
This protocol of TMS is:
To improve outcomes for our patients, we also include cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) as a part of our treatment. When combined with the traditional method of TMS (rTMS), CBT improved response and remission rates by ~8% and ~19%, respectively. Additionally, CBT is likely to produce sustained improvement over time once treatment has concluded.
Our brain stimulation treatment is ideal for most patients with treatment-resistant depression. However, we do not treat patients under the age of 18 or over 65. Additionally, as a safety measure, we do not treat patients who have a history of seizures or who are currently actively suicidal and in need of crisis care.
Click here to learn more about receiving accelerated fMRI TMS therapy at Cognitive FX.

Dr. Mark D. Allen holds a Ph.D. in Cognitive Science from Johns Hopkins University and received post-doctoral training in Cognitive Neuroscience and Functional Neuroimaging at the University of Washington. As a co-founder of Cognitive Fx, he played a pivotal role in establishing the unique and exceptional treatment approach. Dr. Allen is renowned for his pioneering work in adapting fMRI for clinical use. His contributions encompass neuroimaging biomarkers development for post-concussion diagnosis and innovative research into the pathophysiology of chronic post-concussion symptoms. He's conducted over 10,000 individualized fMRI patient assessments and crafted a high-intensity interval training program for neuronal and cerebrovascular recovery. Dr. Allen has also co-engineered a machine learning-based neuroanatomical discovery tool and advanced fMRI analysis techniques, ensuring more reliable analysis for concussion patients.

If you’re considering brain stimulation therapy for treating major depression, you may wish to understand the differences between repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) and deep...

For many people living with major depression, antidepressant medications either don’t work or only get them part of the way to recovery. Symptoms may ease for a while, but then return, or never fully...

While many people are learning about Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) for the first time, this brain stimulation method has been helping patients for nearly 40 years. Originally developed as...

If you’re considering transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) therapy, you may be concerned about its side effects and whether the benefits outweigh any risks.

To understand why your depressive symptoms aren’t going away, it’s important first to recognize that major depression is a complex disorder influenced by various factors. Effective treatment requires...

Intermittent theta burst stimulation (iTBS) has been growing in popularity since receiving FDA approval for treating major depression in 2018. This new brain stimulation method uses a series of...
Published peer-reviewed research shows that Cognitive FX treatment leads to meaningful symptom reduction in post-concussion symptoms for 77% of study participants. Cognitive FX is the only PCS clinic with third-party validated treatment outcomes.
READ FULL STUDY